
/BurnScars-5b5f79bc46e0fb00251463a2.jpg)
(except during bathing and massage) for a period of at least 9–12 months to be of benefit.
#ROAD BURN SCARS SKIN#
As the skin toughens, the commercial pressure garments may be prescribed. For this, initially gentle pressure is applied with crepe bandages. Before prescribing commercial pressure garments, the newly healed skin must be preconditioned to accept the stress and pressure exerted by the garments. The effectiveness of these garments decreases after the development of hypertrophic scars. The compression garments prevent the development of hypertrophic scars. These unsightly scars are hyperaemic, raised above the surface of skin, firm to hard in consistency and itchy. Very frequently, they develop hypertrophic scars. The favourable maturation of scars is also greatly helped by using custom-made pressure garments, especially for deep dermal burns and donor sites of intermediate and thick split-skin grafts which involve reticular dermis. This can be done by coverage with clothes, caps, sun screen lotions with SPF of at least 20–25, decreasing outdoor activity during daytime or even using an umbrella. The healed areas must also be prevented from exposure to sunlight till they are mature, to prevent hyperpigmention. Massage with steroid containing creams may also be advised for short periods on areas which can be protected from exposure to sunlight as otherwise hyperpigmentation can result. Gabapentin and its analogue, pregablin, have shown promising results in relieving this pruritis. Itching must be prevented not only to make the patient comfortable but also to break the cycle and ulceration. Most of these patients complain of itching on the healed burn and split-skin donor sites and need prescription of antihistaminic drugs (pheniramine maleate, promethazine, etc.) as well at least at bed time. The overuse of lubricants is avoided as this may lead to furuncles.
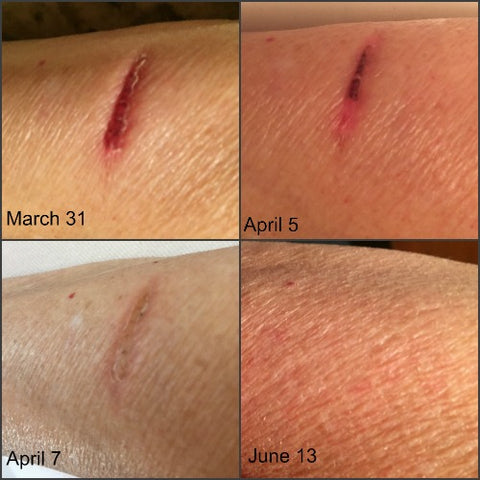
In all these cases, the scar is immature and measures are taken to allow the scar to mature favourably.Īll the healed burnt areas as well as the donor sites tend to be dry and use of emollients is suggested and it helps in keeping the area supple and also reduces the burn itch. In a healed burn patient, the healing may have occurred either spontaneously with epithelialisation from remnants and contraction from wound margins or by split-skin grafting after early excision or over granulating raw areas after spontaneous eschar separation. The extent and magnitude of scarring is directly related to the severity of burn injury. Post-burn hypertrophic scar on anterior chest wall. Scar contracture, on the other hand, is the end result of the process of contraction. Wound contraction involves an interaction of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts and collagen deposition and is a satisfactory mechanism when the tissue loss is small, in a non-critical area and surrounded by loose skin. The reduction in size of wound causes lesser degree of connective tissue deposition and the amount of epithelialisation needed is decreased.
#ROAD BURN SCARS FULL#
With full thickness loss of skin, wound contraction and epithelialisation from the margins occurs leading to contractures.Ĭontraction is an active biological process by which an area of skin loss in an open wound is decreased due to concentric reduction in the size of the wound. The final result is demonstrated by a lesser or more extensive formation of the cicatrix.

If the skin is affected deeper in the zone of stratum reticulare, the defect is covered by substitutive unspecialised connective tissue. The sequence of cellular events that comprise epithelialisation include cellular detachment, migration, proliferation and differentiation. These appendages extend into the deeper dermis and may even penetrate into the subcutaneous fat (as in beard area in males) and survive in partial thickness injuries. The epithelial cells, in these cases, are derived from the epithelial appendages such as pilosebaceous units and sweat glands in the central portion and wound edges at the periphery.

Restitution is possible only if the skin is burnt as deep as the stratum papillare and all the specialised cells of the organ are preserved. The healing of a burn wound is accomplished either by restitution (complete regeneration) or substitution. BURN WOUND HEALING AND DEVELOPMENT OF SCAR AND SCAR CONTRACTUREĪn understanding of the burn wound healing is fundamental not only to the management of the acute burn wound, but also for the prevention, minimisation and treatment of post-burn scars and scar contractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
